Understanding Graduation Rates
About 1.2 million students fail to graduate from high school in the
The report, Understanding High School Graduation Rates, highlights the discrepancies between how the government and independent sources report graduation rates and evaluates the effectiveness of each state's current data collection and accountability systems.
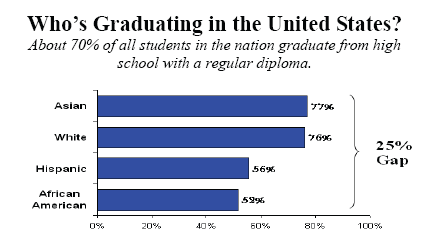
According to the brief by the Washington-based group, there is a 13 percent reporting gap in graduation rates between state, federal and independent sources. Yet, this gap ranges from a low of 4 percent to a high of 32 percent. In
The
Among their recommendations are:
-
Use of common, accurate graduation rate calculations. In 2005, all fifty governors signed a National Governors Association's Graduation Rate Compact where they pledged to adopt accurate and consistent measures for high school graduation. Yet there are still eight different types of graduation rates being used by states.
-
Track individual student data from the time students enter the educational system until they leave it. The Data Quality Campaign, a national effort to support states in improving the collection and reporting of data, has recommended ten essential elements of a rigorous longitudinal system. Many states are working to implement these, but only one has all ten elements in place currently, and only sixteen have at least four.
-
Meaningful goals improving student achievement. Only four states have set a graduation rate goal of 100 percent, and most states permit schools to meet their Annual Yearly Progress with as little as a 0.1 percent improvement or less each year.
Published Thursday, May. 3, 2007